Special Reports are longer, often more technical, documents consisting of entire articles, government statements, and other documents relevant to security and peace in Northeast Asia.
Japan’s Signals Intelligence (SIGINT) Ground Stations: A Visual Guide
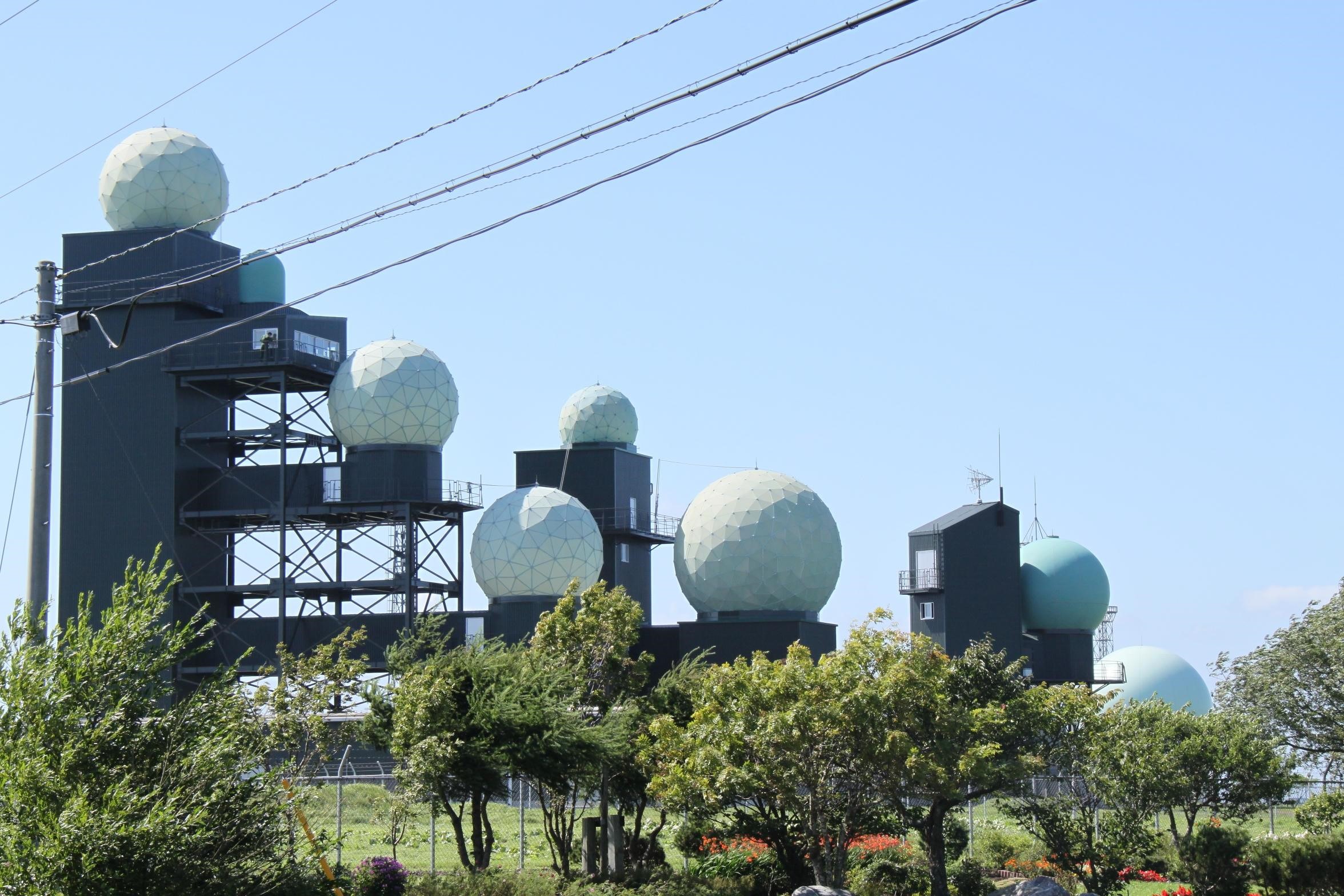

This is a study of Japan’s ground-based signals intelligence (SIGINT) stations, the 17 (soon to be 19) major f…
Go to the articleAn Updated Estimate of Energy Use in the Armed Forces of the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (DPRK)

North Korea’s new leader inherited a large standing conventional military. Shortly after taking over, he succeeded in launching a rocket and testing a nuclear device. His actions were likely primarily driven by domestic concerns. North Korea’s governance system seems to seek strong domestic support in part by being able to demonstrate a set of strong external forces allied against the nation, which helps to make acceptable the consolidation of decision power under one charismatic leader and justifies diverting a larger portion of the populace away from the civilian sector of the economy and into the military than is the case in any other country. This large standing conventional force demands a surprisingly modest proportion of North Korea’s overall energy usage (though a much larger fraction of the DPRK’s limited petroleum fuels supplies) indicating a large, but not particularly active military. Despite increased tensions in recent years, it is not clear that North Korea’s military has actually increased its overall energy demand. North Korean military energy usage seems more or less static over the years and is consistent with observations that North Korean rhetoric regarding potential military actions has increased, but that the actual actions of the DPRK’s conventional military remain muted.
Go to the articleEnergy Security and the Role of Green Economies in East Asia
by David von Hippel Contributing authors: Yi Wang, Kae Takase, Tetsunari Iida, Myungrae Cho, and Sun-Jin Yun 28 July 2015 I. Introduction David von Hippel writes that following the Fukushima nuclear disaster, there is an increasing ‘recognition that new paradigms are needed to deal with expanding complexity in the relationships between the issues and actors […]
Go to the articleGlobal Problems, Complexity, and Civil Society in East Asia

by Peter Hayes and Richard Tanter 13 July 2015 I. INTRODUCTION This Special Report is an extract (Chapter 2) to the book Complexity, Security and Civil Society in East Asia, edited by Peter Hayes and Yi Kiho, published by Open Book Publishers in June 2015 (http://www.openbookpublishers.com/product/326/). To read the entire book or download the free PDF […]
Go to the articleComplexity, Security and Civil Society in East Asia – Preface and Introduction

by Peter Hayes, Yi Kiho and Joan Diamond 2 July 2015 I. INTRODUCTION This Special Report is an extract (Preface and Introduction) to the book Complexity, Security and Civil Society in East Asia, edited by Peter Hayes and Yi Kiho, published by Open Book Publishers in June 2015 (http://www.openbookpublishers.com/product/326/). This book is devoted to improving our understanding […]
Go to the articleThe corporatisation of Pine Gap

by Desmond Ball, Bill Robinson, Richard Tanter, and Philip Dorling 25 June 2015 The full PDF version of this report is available here I. Introduction The Joint Defence Facility Pine Gap, located just outside the town of Alice Springs in Central Australia and managed by the U.S. National Reconnaissance Office (NRO), is one of the largest […]
Go to the articleExpanded Communications Satellite Surveillance and Intelligence Activities Utilising Multi-beam Antenna Systems
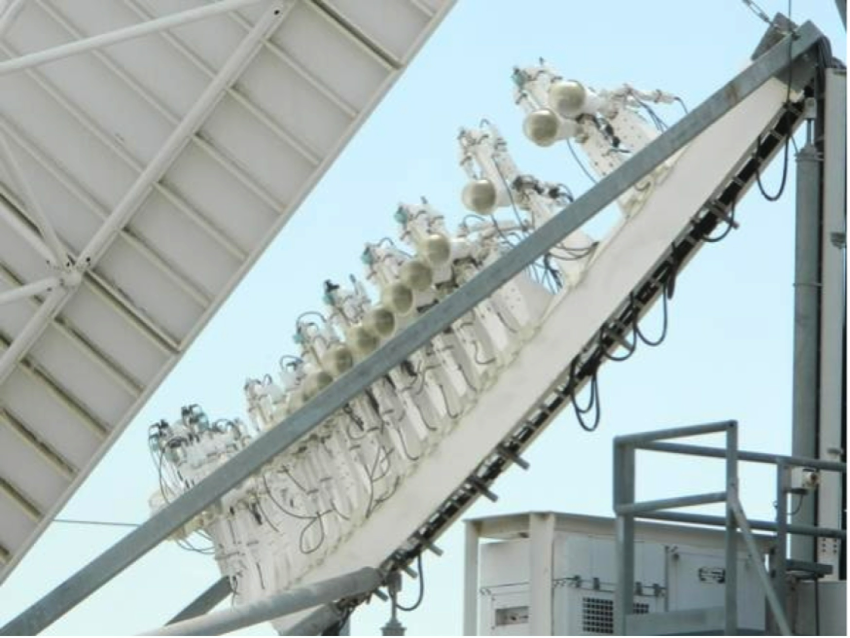

by Desmond Ball, Duncan Campbell, Bill Robinson and Richard Tanter 28 May 2015 The full report is available here. I. Introduction The recent expansion of FORNSAT/COMSAT (foreign satellite/communications satellite) interception by the UKUSA or Five Eyes (FVEY) partners has involved the installation over the past eight years of multiple advanced quasi-parabolic multi-beam antennas, known as Torus, […]
Go to the article북한의 핵무기 개발과 능력

이 춘 근 (과학기술정책연구원 연구위원) 11 May 2015 English version (영어 버전) here http://www.kdjlibrary.org/ 요약 이춘근 한국 과학기술정책연구원 선임연구위원은 글에서 ‘북한은 수십 년의 노력을 거쳐 국내산 원료를 사용하는 원자력 주기를 완성하였다’고 하고 ‘북한의 핵무기는 … 각종 부품과 재료, 기술이 부족하’지만 ‘자력갱생으로 이러한 난관들을 상당히 극복했’다고 분석한다. 이 연구위원은 ‘북한의 핵 관련기술 개발과 수준에 대한 보다 […]
Go to the articleAssessing North Korea’s Nuclear Weapons Capability

by Lee Chun-keun 11 May 2015 For the Korean language version of this report click here. I. Introduction Lee Chun-keun writes that ‘North Korea, after decades of effort in its nuclear endeavor, has managed to develop its nuclear program using homegrown resources.’ He states that while North Korea’s ‘nuclear weapons program…lacks parts, resources and technology to […]
Go to the article동북아 핵안전 보장: 동북아 핵안전 장치에 대한 한국의 제안
박윤원 5 May 2015 English version (영어 버전) here http://www.kdjlibrary.org/ 요약 박윤원 교수는 한국, 중국, 일본에게 주어진 핵에너지 사용의 불가…
Go to the article
