North Korean Trade with China as Reported in Chinese Customs Statistics: 1995-2009 Energy and Minerals Trends and Implications
By Nathaniel Aden
June 7, 2011
This paper was originally published as part of a special issue of the Korean Journal of Defense Analysis (Volume 23 Number 2 Summer 2011) on the DPRK Energy and Minerals Sectors.
The papers in this series were adopted from research presented at the Nautilus Institute’s 2010 DPRK Energy and Minerals Working Group Meeting in Beijing.
Additional papers from this workshop are available here.
Nautilus invites your contributions to this forum, including any responses to this report.
——————–
CONTENTS
VI. Nautilus invites your responses
Nathaniel Aden, Senior Research Associate with the Lawrence Berkeley Lab China Energy Group, writes, “China is North Korea’s largest international trading partner…Whereas North Korean electricity and iron ore exports are sold at sub-market “friendship prices,” Chinese coal and oil products have been sold to North Korea at premium prices. Chinese Customs data suggest that Beijing is taking a pragmatic, market-oriented approach to trade with its reclusive neighbor, while the increasingly asymmetrical energy embodiment of bilateral trade may reflect dilapidation of North Korea’s non-military industries.”
The views expressed in this article are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of the Nautilus Institute. Readers should note that Nautilus seeks a diversity of views and opinions on significant topics in order to identify common ground.
II. Article by Nathaniel Aden
-“North Korean Trade with China as Reported in Chinese Customs Statistics: 1995-2009 Energy and Minerals Trends and Implications”
By Nathaniel Aden
1.Introduction
The People’s Republic of China (PRC) ranks as the largest international trade partner of the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (DPRK) [1]. In 2009, the DPRK’s bilateral trade with the PRC was more than 100 times larger than total U.S. assistance to North Korea [2]. Insofar as they provide “mirror statistics,” bilateral trade data offer a glimpse into the changing PRC-DPRK relationship, as well as into the internal dynamics of North Korea’s energy system and economy. In the absence of published, reliable North Korean data on its domestic energy system, economy, and foreign policy, Chinese bilateral trade data are an accessible, internally-consistent source of information.
2.Data Sources for DPRK Trade
North Korean trade data are compiled by partner-country Customs Bureaus, the United Nations (UN), and the International Energy Agency (IEA). The IEA publishes production, consumption, and trade data in their annual Energy Balances of Non-OECD Countries series. As North Korea’s largest trading partners, China and Republic of Korea (ROK) customs data provide the most extensive source of “mirror statistics” on the DPRK’s economic activities, since the DPRK publishes few, if any, statistics of its own. Chinese data are compiled and published by the China Customs Bureau, and South Korean data are controlled by the Korean Trade-Investment Agency (KOTRA). Each dataset presents a different picture of DPRK trade due to the variety of sources and methodologies. In order to explore the PRC-DPRK relationship and its implications, this report analyzes Chinese Customs statistics.
Chinese Customs data describe the value and quantity of bilateral trade with the DPRK as classified by the World Customs Organization’s Harmonized System (HS) codes. These data were accessed through the World Trade Atlas. All price and value data are presented in nominal US dollars according to monthly exchange rates of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, and adjusted for presumed CIF (cost, insurance, and freight) charges. [3] Quantity data are presented in metric tonnes, megawatt-hours (MWh), or discrete units (e.g., number of cars, bicycles, etc.), as noted. Unless otherwise noted, data in the text and figures of this report are sourced from the China Customs Bureau.
There are limitations in the degree to which China Customs data can be used to understand the bilateral relationship between the two countries, much less the dynamics of North Korea’s physical and political economy. Incomplete coverage and potential reporting bias are two basic limitations of China Customs data. By virtue of their focus on merchandise trade, customs data do not include aid shipments, official development assistance (ODA), direct government transfers, foreign direct investment, services, remittances, barter trade, smuggling, illicit trade, and trade in military equipment. Explosives, arms, and ammunition trade is covered in Chinese Customs data. Reported Chinese trade with the DPRK in these categories, however, clearly do not include military equipment, as reported North Korean exports are nil and imports only amounted to $530,000 in 2009–less than 10% the value of umbrella and walking stick imports. Chinese reporting bias is difficult to detect given the lack of published North Korean data on bilateral trade with which to compare it. The China Customs Bureau, however, clearly and purposely obfuscated its bilateral trade relationship in 2009 when it categorized North Korea under the category “Other Asia, Not Elsewhere Specified” during the period from August through November. [4] The rationale for this four-month re-classification is unclear, especially given the consistency of trade flows throughout this period; no other countries appear to be included in the 2009 “Other Asia, N.E.S.” data. This analysis incorporates “Other Asia, N.E.S.” data in all 2009 analysis of China-DPRK bilateral trade.
3.The DPRK’s Trade with China: Fuels and Energy Commodities
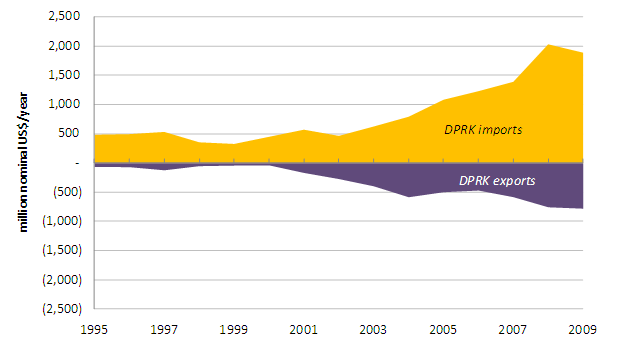
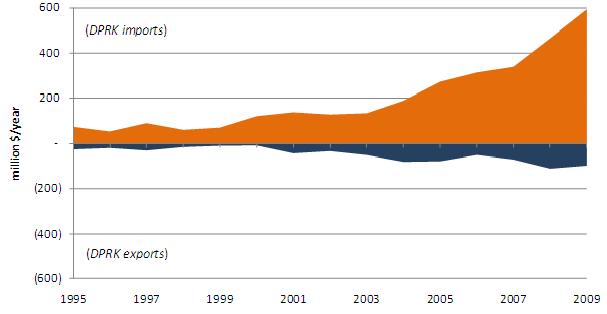
After diminishing in the late 1990s, the annual value of total DPRK-PRC bilateral trade has grown from a fourteen-year low of $370 million nominal dollars in 1999 to a high of $2.8 billion dollars in 2008. In 2009 the value of aggregate North Korean-Chinese bilateral trade dropped slightly to $2.7 billion. Between 2000 and 2009 North Korean imports of Chinese merchandise grew at an average annual growth rate of 17%, from $450 million in 2000 to $1.9 billion in 2009; over the same period, the nominal value of DPRK exports to China increased at an average annual growth rate of 40%, from $37 million in 2000 to $780 million in 2009. Figure 1 illustrates the value of DPRK bilateral trade with China. The dominance of the orange area highlights North Korea’s ongoing trade deficit with China, which grew from $410 million in 2000 to a fourteen-year high of $1.3 billion in 2008.
Figure 1: Annual Nominal Value of Bilateral DPRK-PRC Aggregate Trade (1995-2009)
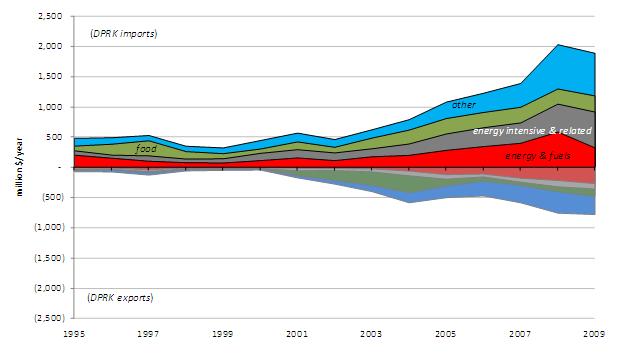
Energy has played a significant, but generally diminishing, role in reported commercial trade between China and North Korea. As highlighted by the red area of Figure 2, North Korea has been a consistent net importer of energy and fuels from China in value terms. [5] However, energy and fuels’ share of DPRK imports diminished from 26% of total value in 2000 to 17% in 2009, as imports diversified to include more energy-intensive and related goods (grey area in Figure 2), food (green area), and other merchandise (blue area). [6] Among North Korean exports to China, the value of energy and fuels exports has grown from 9% of total export value in 2000 to more than 33% in 2009.
Figure 2: Composition of Total Annual DPRK-PRC Trade by Value (1995-2009)
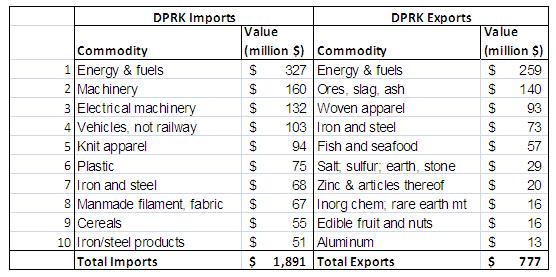
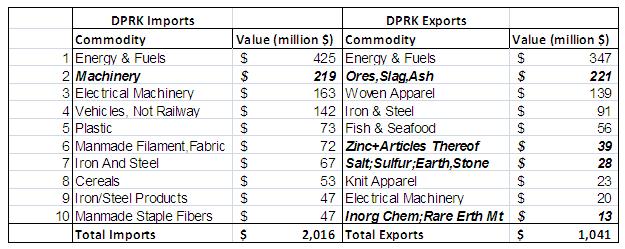
The $140 million (7%) drop of the value of North Korean imports between 2008 and 2009 was driven by a reduction in both the unit price and the quantity of energy and fuels and–to a limited extent–the reduced value of “other” imports. Increases in the value of energy-intensive and related goods and food imports from 2008 to 2009 were offset by diminished costs for fuel and other imports. Table 1 provides a snapshot of the role of energy in bilateral trade in 2009. The lower value of energy and “other” North Korean imports in 2009 was driven by reductions of both volumes and prices from 2008 levels.
Table 1: Top-Ten DPRK Imports from and Exports to the PRC by Value (2009) [7]
Whereas North Korean imports of food from China comprised three of the top ten import commodity categories (worth $115 million) in 2007, food, in the form of cereals, comprised only one of the top ten import categories in 2009. Meat imports were overtaken by North Korean demand for Chinese light manufactured products in the form of knit apparel, manmade filaments, and fabric. On the export side, DPRK exports became more mineral- and resource-intensive with the growth of salt, sulfur, earth, stone, inorganic chemical, rare earth metals, and aluminum exports in 2009.
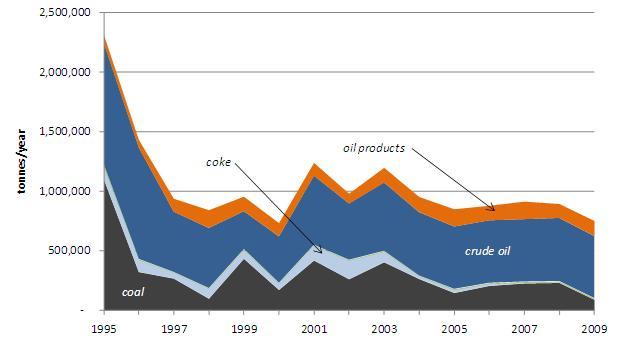
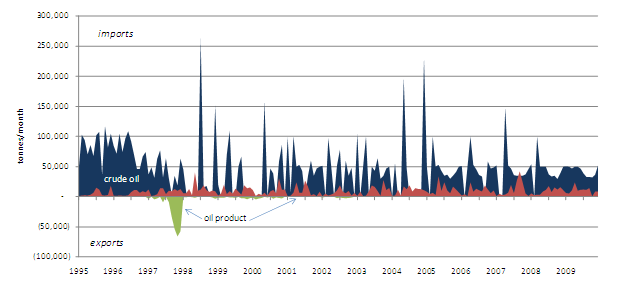
The quantity of North Korean coal imports from China dropped from 230,000 tonnes in 2008 to 90,000 tonnes in 2009, thereby comprising 12% of annual fuel imports by mass. Reductions in crude oil and coal shipments from China have led the decline of DPRK fuel import quantities, which fell at an average rate of 8% between 1995 and 2009, though the bulk of this decline took place between 1995 and 1997. Oil product imports have countered the trend of decline, with oil products imports from China expanding from 73,000 tonnes in 1995 to 130,000 tonnes in 2009.
The ongoing decline of energy import volumes in the face of increasing overall imports and trade likely reflects the DPRK’s demand sensitivity to increased international market prices and/or North Korea’s lack of foreign currency with which to purchase energy and fuel imports. Figure 3 illustrates the decline of North Korean fuel imports from China by volume.
Figure 3: Annual Volume of Selected DPRK Primary Energy Fuels Imports from PRC (1995-2009) [8]
Note: Figure 3 does not include electricity imports.
Aside from a brief peak of 240,000 tonnes of oil product in 1997 (48% of which was fuel oil and 39% naphtha by mass), North Korea’s energy and fuels exports to China were negligible until 2001, when coal exports began to grow rapidly. Figure 4 illustrates the quantity of North Korean energy and fuel exports to China, and particularly the rapid expansion to 3.7 million tonnes of coal exports in 2007. Energy content, usage, and value vary among the major fuels discussed here; it is noteworthy, however, that North Korea has been a net exporter of fuels by mass since 2004.
Note: Figure 4 does not include electricity exports.
The mass of North Korean coal exports to China from 2007 through 2009 (9.9 million tonnes) exceeded the total quantity of exports over the previous eleven-year period. In 2009 the quantity of North Korean coal exports was almost five times the total quantity of all coal, coke, crude oil, and oil product imports from China to the DPRK. Although petroleum has a higher energy density than coal, North Korea has been a net exporter in terms of the energy content of bilateral fuels trade since 2004. [9]
Figure 5: Annual Value of Selected DPRK Primary Energy Fuels Trade with PRC (1995-2009)
Note: Figure 5 does not include electricity imports.
Although North Korea has been a net energy exporter in its fuels trade with China since 2004, it has also been a continuous exporter of money in its bilateral fuel trade with China since 1995. Figure 5 shows the annual value of bilateral fuels trade. Until 2009, the DPRK spent an increasing amount of money on diminishing quantities of fuel imports. The drop of oil prices from 2008 to 2009, and the relative rise of coal prices paid by China in 2008 and 2009, reduced North Korea’s bilateral trade deficit with respect to fuel imports and exports to a 14-year low of $68 million in 2009.
3.1Major petroleum products trade
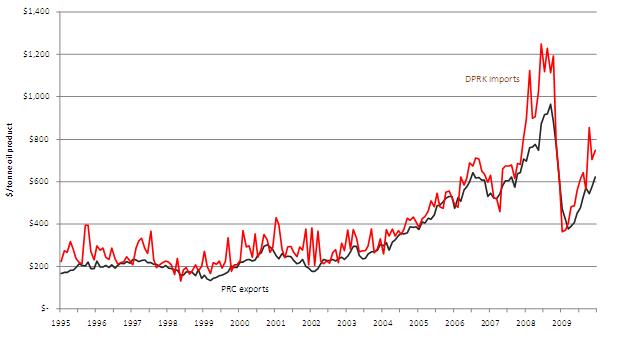
Between 2000 and 2008, North Korean expenditures on imported Chinese crude oil increased more than five-fold, while the quantity of crude oil imports increased by 36%. Between 2008 and 2009 the quantity of crude oil imports fell 2% while the value dropped 42% as a result of the fall in international oil prices. Over the first decade of the 21st century, the quantity of DPRK oil product imports increased 14% while their value more than doubled (between 2000 and 2009). Figure 6 shows the monthly volumes of DPRK-PRC crude oil and oil product trade. Aside from a brief flurry of product exports between October and December, 1997, North Korean oil products exports have been negligible. With the exception of a one-month interruption in February 2008, the flow of crude oil from China to North Korea has become more stable and sustained since March of 2007, though in recent years through 2009 the annual quantity of crude oil imports remained about half the 1995 level. Unlike crude oil, the flow of oil product has not been interrupted since 1995. In 2009 43% of oil product imports were motor gasoline and aviation gasoline (HS category 27101110) and 39% were aviation kerosene (HS 27101911) by mass. Although monthly oil product levels are somewhat erratic, annual North Korean imports of Chinese oil products have remained fairly level, with a 1% average annual growth of volume between 2000 and 2009.
The data shown in Figure 6 indicate that North Korea’s crude oil production capacity is lower than domestic demand, and possibly non-existent. While still lower than 1995 levels, crude oil imports expanded at an average annual growth rate of 3% between 2000 and 2009, suggesting that North Korea has relatively stable oil refining capacity in the refinery that accepts Chinese crude. On the downstream side, oil product imports, combined with rising motor vehicle imports, suggest that North Korea’s road transport sector is growing, or at least that the share of imported vehicles in the DPRK road transport sector is increasing.
3.2Coal and other solid fuels trade
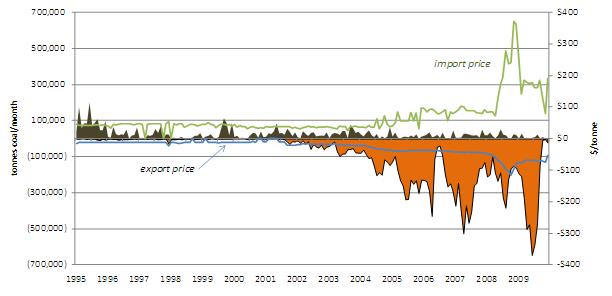
In 2009 North Korean imports of Chinese coal dropped to their lowest level in fourteen years–90,000 tonnes. In the same year North Korea exported 3.6 million tonnes of coal to China, up from 8,000 tonnes in 2000. Figure 7 illustrates the gradual decline of North Korean coal imports and the rapid growth of exports, as well as the sharp rise and fall of coal prices in 2008.
The past fifteen years of PRC-DPRK coal trade are bisected into two periods by China’s accession to the World Trade Organization (WTO) in December 2001. Prior to China’s WTO accession, the DPRK was a net coal importer, with the price of its limited exports remaining fairly fixed around $12/ton during the mid-1990s. Areas on the chart in which prices drop to zero do not indicate free coal transfers; rather, they illustrate interruptions in trade volumes. After China’s WTO accession, DPRK export prices for coal began to rise, though not as quickly as export volumes. North Korea became a net coal exporter in 2002; by 2009, the DPRK exported nearly 40 times more coal than it imported. In 2008 the average annual price of DPRK coal exports climbed to $77 per tonne and the price of imported Chinese coal shot up to $192 per tonne. The bilateral relationship echoes China’s global coal trade position in the sense that China’s total coal export volumes to all countries dropped at an average annual rate of 10% between 2000 and 2008, while its imports from all countries have grown at 58% per year over the same period. One interpretation of North Korea’s coal export surplus is that it represents barter payment for access to Chinese oil, equipment, and capital. [10]
3.3Electricity trade
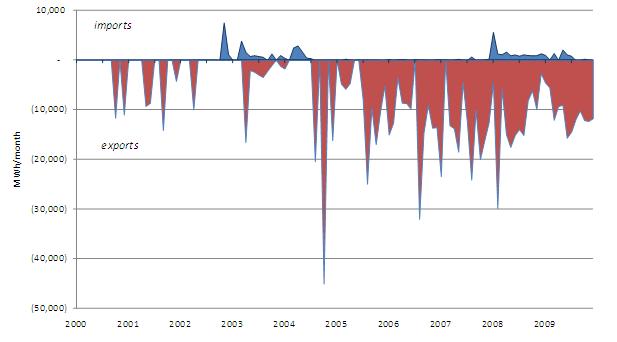
Bilateral electricity trade, or at least recorded trade, did not commence until the end of 2000, when sporadic exports of power from North Korea began to appear in China’s customs statistics. North Korean imports of Chinese electricity have been minimal and sporadic, with 2009 imports amounting to 6.9 GWh versus 130 GWh of exports. Figure 8 illustrates the monthly volumes of bilateral electricity trade since 2000. The volume of North Korean electricity exports to China grew at an average annual growth rate of 21% between 2000 and 2009. Electricity exports were uninterrupted from February of 2007 through the end of 2009. The International Energy Agency reports that North Korea’s total electricity generation amounted to 21,500 GWh in 2007 (IEA, 2009); China Customs data indicate that North Korea exported 0.8% of total generated electricity to China in 2007.
Figure 8: Monthly Amount of DPRK-PRC Electricity Trade (January 2000-December 2009)
The regular peaking of DPRK electricity exports in August suggests two possible explanations: hydropower capacity comes online with summer snowmelt and rainfall, and/or North Korean generators are responding to heightened Chinese demand for electricity in hot summer months. The reported value and quantity of DPRK electricity exports indicate that prices paid by China for power from the DPRK are closely controlled and in fact, from January through December 2009, were fixed (see Figure 11, below). Likewise, the increasingly sustained and higher-volume electricity exports since 2005 suggests the completion of additional DPRK hydropower capacity to serve Chinese border areas and/or the shifting of DPRK near-border electricity output to serve export, rather than domestic, markets. The barter theory—that energy is being exported from North Korea in exchange for oil, capital, and equipment—is further bolstered by the 41% annual growth of small-scale electricity generator set imports between 2005 and 2008. [11] Exporting electricity while importing generator sets also suggests that the North Korean transmission and distribution grid has likely become dilapidated, and that close-to-border electricity production helps feed bilateral barter trade. Further evidence of DPRK grid dilapidation comes from the juxtaposition of per capita electricity use and electricity exports. Estimated per-capita electricity consumption in the DPRK dropped from 820 kWh in 2005 to 760 kWh in 2007, at the same time that exports to China grew from 90 to 170 GWh (IEA, 2009). As such, expanded electricity exports are not likely to mitigate, but in fact may accelerate, the DPRK’s ongoing rural energy crisis. [12]
3.4Energy pricing and key implications of energy trade data
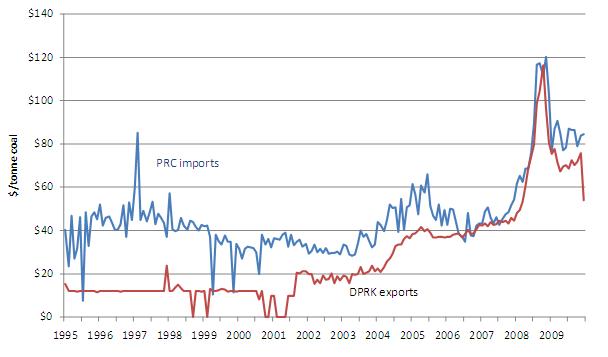
Beyond the value and volume of bilateral trade flows, energy prices reveal the increasingly pragmatic, market-oriented character of China’s economic relationship with North Korea. Figure 9 shows the average monthly price per tonne for Chinese imports of coal from all countries including North Korea (blue line), and the average monthly price for DPRK coal exports to the PRC (red line). Whereas the DPRK used to sell coal to China at stable, discounted prices, post-2007 trade data appear to indicate that North Korean export prices are tracking the world market more closely. An important caveat to these observations is that the coal data in Figure 9 aggregate anthracite, bituminous, and lignite fuels and therefore do not necessarily have the same energy content for different sources or in different years.
Figure 9: Monthly Average DPRK Coal Export Prices (for PRC) Compared to Overall PRC Coal Import Prices (January 1995-December 2009)
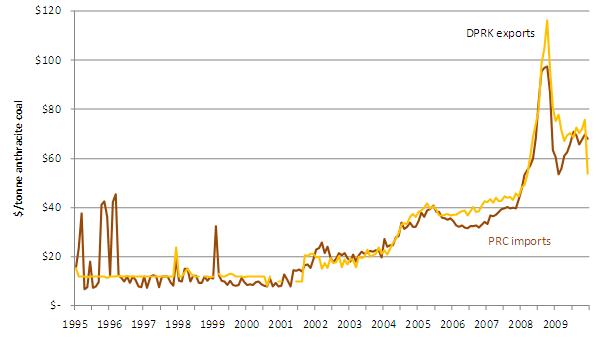
Aside from North Korean “friendship pricing” (which appears to have been fixed around $12 per ton until the end of 1997), there are three other likely factors that may explain the coal pricing differential. First, the methodology used for reporting trades may be inconsistent: imports may be recorded at higher c.i.f. prices, while exports are calculated f.o.b. Second, geography and infrastructure may generate asymmetries: North Korean coal mines may be closer to Chinese buyers and/or North Korea may have lower transportation costs. However, the factor most likely to explain DPRK-PRC coal price differentials is the varying energy composition of bilateral trade flows—North Korean coal exports were entirely composed of anthracite coal in 2009, while North Korean imports were 93% bituminous coal by mass. Anthracite coal is more dense and often burned for power generation, while bituminous coal has a range of uses including power generation and coking. In order to eliminate the anthracite-bituminous factor in Sino-DPRK coal price differentials, Figure 10 compares prices for anthracite trade alone.
Disaggregation of coal trade reveals that North Korea actually earns above-market prices for their anthracite coal exports to China. In 2000 North Korean anthracite coal was exported to China for prices that were 28% higher than other Chinese anthracite coal imports. The DPRK price premium declined to 13% in 2007 and 10% in 2009. The juxtaposition of Figure 9 and Figure 10 shows that the earlier “friendship price” differential is largely explained by the composition of coal trade–i.e., China’s 2009 global coal imports were only 27% anthracite (which is cheaper than bituminous coal) by mass. [13] Nevertheless, the trajectory of DPRK anthracite prices suggests increased market orientation, diminishing North Korean anthracite quality (that could otherwise continue to command a price premium), and/or more competition for supplying anthracite coal to Northeastern China (perhaps due to improved Chinese rail infrastructure). Anthracite coal has a calorific value greater than 23.9 MJ/kg, but includes a range of heat values up to 33 MJ/kg; another explanation of the anthracite price differential is that North Korean anthracite is of higher quality than other Chinese anthracite sources.
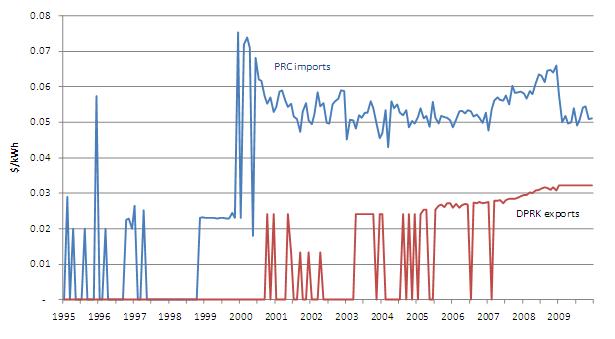
Figure 11: Average Monthly DPRK Electricity Export Prices Compared to Overall PRC Electricity Import Prices (January 1995-December 2009)
Whereas North Korean anthracite coal is exported to China at market or even premium prices, North Korean electricity is sold to China at highly discounted prices. However, the rate of discount for North Korean electricity relative to other sources of Chinese electricity imports is declining: it dropped from 50% in 2007 to 38% in 2009 as DPRK electricity export prices crept up from 28 to 32 Mills per kilowatt-hour over the same period. [14] Besides “friendship pricing” by North Korean electricity exporters, the consistent difference displayed in Figure 11 may also be due to fixed prices from joint Sino-DPRK hydropower development projects and/or the intermittency or low quality of North Korean electricity exports. In this vein, the lack of electricity export interruptions after February 2007 may partially explain rising North Korean prices.
Figure 9, Figure 10, and Figure 11 examined the level and trajectory of North Korean export prices compared to Chinese import prices for the same commodities. On the other side of bilateral energy trade, PRC export prices of commodities for which North Korea is a net importer show different patterns. In turning to the Chinese export side of bilateral energy trade, the initial question is whether North Korean “friendship prices,” insofar as they were rooted in government beneficence, have been reciprocated by Chinese exporters.
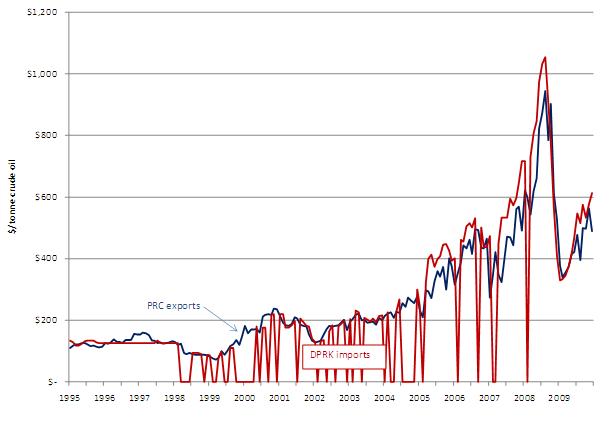
Since 1995 the DPRK has been a consistent importer of Chinese crude oil. Until February 1998, North Korea paid a fixed price of $126.70 per tonne of Chinese crude oil. Once prices were freed, DPRK import prices generally exceeded aggregate average PRC crude oil export prices. In 2008 and 2009, North Korean crude oil imports were 12% and 8% more expensive per tonne than average Chinese crude oil export prices. Interruptions of DPRK crude oil imports became more brief and less common since 2005; imports were uninterrupted from March 2008 through 2009. Figure 12 shows the variation of prices for North Korean imports of Chinese crude oil.
The DPRK has consistently paid premium prices for Chinese oil product exports since 1995. The North Korean price premium for Chinese oil product varied from 7% in 2007 to 26% in 2008, and 16% in 2009. The consistent price differential may reflect lack of surplus in China’s oil product markets, intentionally discriminatory pricing by Chinese exporters, geography, transport costs, quality differentials, risk premiums for exporting to North Korea in the face of undeveloped credit mechanisms, and/or political constraints on North Korea’s ability to import oil product from other sources.
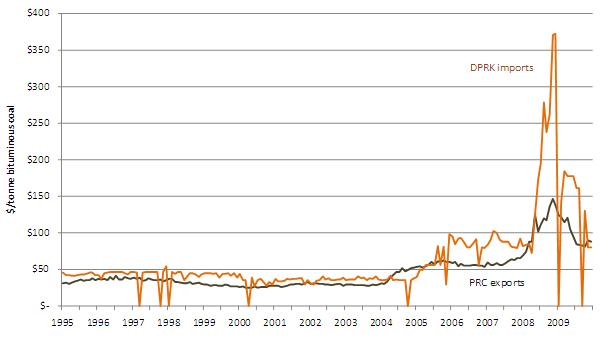
Figure 14: Average Monthly DPRK Bituminous Coal Import Prices Compared to Overall PRC Export Prices (January 1995-December 2009)
In 2009, 93% of DPRK coal imports from the PRC were bituminous coal. The data in Figure 14 tell the same asymmetrical pricing story as PRC-DPRK crude oil and oil products trade. North Korea paid a price premium for bituminous coal exports from China ranging from 33% in 2000 to 48% in 2007 and 58% in 2009. The price rise and supply interruptions in January and September 2009 are likely a result of market tightness in Northeastern China and/or North Korea’s inability to procure bituminous coal from other sources.
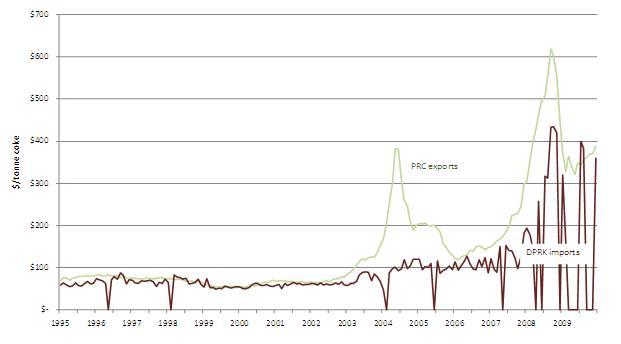
Among energy and fuels for which North Korea is a net importer of Chinese commodities, the coke trade is anomalous insofar as the DPRK has paid discounted prices. Figure 15 illustrates the average monthly coke prices for aggregate Chinese exports and North Korean imports. One possible explanation for the low coke prices is that a significant portion of North Korea’s steel production is controlled by Chinese interests able to command discounts. Although North Korea has received coke imports from China at prices lower than other Chinese exports, trade was interrupted for seven months of 2009. Again, it is difficult to disentangle the international roots of trade interruptions from high domestic Chinese demand for coke due to booming steel production.
Figure 15: Average Monthly DPRK Coke Import Prices Compared to Overall PRC Export Prices (January 1995 – December 2009)
Aside from politically-determined pricing, there are several factors that may help to explain the divergence of North Korean prices from overall Chinese prices for the same commodity. Geography, transport costs, demand, and quality factors have been reviewed above. Another possible explanation is the degree of centralized political control of local exporters and importers. Low DPRK export prices may reflect Pyongyang’s insulation from market prices and/or a lag in transmitting market price information to exporting entities. Likewise, premium PRC export prices may reflect the ability of locally-autonomous producers to exploit North Korean ignorance of international market prices and/or economic isolation. With the small (in terms of trade volume) exception of the coke anomaly, differential Sino-North Korean energy pricing illustrates the DPRK’s lack of economic leverage with its closest ally.
4.Minerals trade
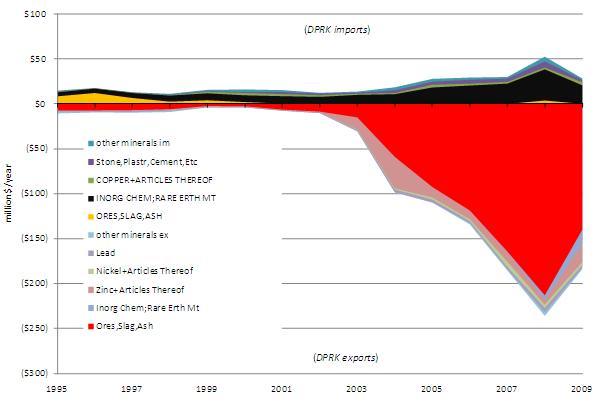
Minerals are a growing driver of bilateral trade, both in terms of North Korean mining equipment imports and minerals exports to China. Between 2000 and 2009 the minerals share of North Korean exports grew from 11% to 24% by value. [15] Figure 16 illustrates the expanding role of minerals in total bilateral trade (brown and black areas of the graph).
Figure 16: Minerals as a Portion of Total Annual DPRK-PRC Trade by Value (1995-2009)
The value of total DPRK minerals exports to China increased by an average annual growth rate of 53% between 2000 and 2009. Trade data do not definitively indicate the degree to which increased mineral exports from the DPRK displaced previous North Korean domestic use or were sourced from expanded domestic production. Nevertheless, the juxtaposition of rapidly growing mineral exports with steadily increasing machinery imports suggests that North Korean mineral mining and processing capacity is expanding. Mineral mining and processing requires a range of equipment that is not covered by any single trade category. Particular categories, however, can serve as useful proxies for estimating the flow of mining-related equipment between China and the DPRK. As illustrated in Table 1 (above) and Table 2, machinery remains the second largest category of North Korean imports from China, behind energy and fuels (largely oil). Within the various machinery trade categories, HS category 8474 covers machinery for sorting, screening, separating, washing, or crushing earth, stone, or mineral substances, and shaping or molding mineral products. The value of North Korea’s HS 8474 imports boomed from $210,000 in 2000 to more than $22 million in the first eleven months of 2010.
Table 2: Top-Ten DPRK Imports and Exports to the PRC by Value (first 11 months of 2010)
Table 2 lists the ten largest HS 2-digit bilateral trade categories for the first eleven months of 2010. During the first six months of 2010 Ores, Slag, and Ash was the largest category of North Korean exports, but a surge in coal exports between July and November brought the ores category back to second place for the year to date. The four mineral export categories listed in Table 2 comprise 29% of total first-eleven-month exports–a notable rise from 24% for all mineral exports in 2009. On the import side of the ledger, machinery comprised 11% of total value of DPRK imports from China in the first eleven months of 2010, up from 3% in 2000.
4.1Metallic Ores
Metallic ores dominate North Korea’s bilateral minerals trade with China in terms of both annual value and mass. Figure 17 illustrates the annual value of bilateral minerals trade between 1995 and 2009. Ores, slag, and ash comprised 76% of 2009 North Korean exports by value, and inorganic chemicals and rare earth metals accounted for 72% of the value of 2009 mineral imports to the DPRK from China.
Figure 17: Composition of Annual DPRK-PRC Minerals Trade by Value (1995-2009)
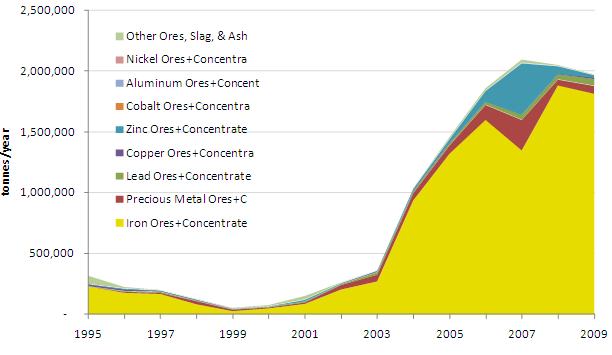
Unlike in aggregate bilateral trade, North Korea is a net exporter of minerals in volume and value terms. Whereas North Korea was a net mineral importer in 2000, the value of mineral exports exceeded imports by more than nine times in the first eleven months of 2010. More than 60% of 2010 DPRK mineral imports were comprised of inorganic chemicals and rare earth metals, which in turn were mostly composed of aluminum oxides and carbonates. While carbonates are the largest category of traded non-metal minerals, their scale was dwarfed by metallic ores. On the exports side of the ledger, ores, slag, and ash comprised 78% of the value of first-eleven-months 2010 minerals exports to China. The rapid growth of North Korean ore, slag, and ash export volumes to China is displayed in Figure 18.
Figure 18: Annual Volume of North Korean Ore, Slag, and Ash Exports to China (1995-2009)
The growth of North Korean mineral exports to China between 2000 and 2010 was driven by Chinese demand for iron ore. Between 2000 and 2009 China steel production grew at an average annual rate of 18%–to 568 million tonnes crude steel in 2009. Over the same period North Korean iron ore exports to China grew at an average rate of 49% per year. In the first eleven months of 2010 iron ore comprised 91% of ore, slag, and ash exports from the DPRK to China, distantly followed by gold and silver metal ores and concentrates.
4.2Mineral Pricing
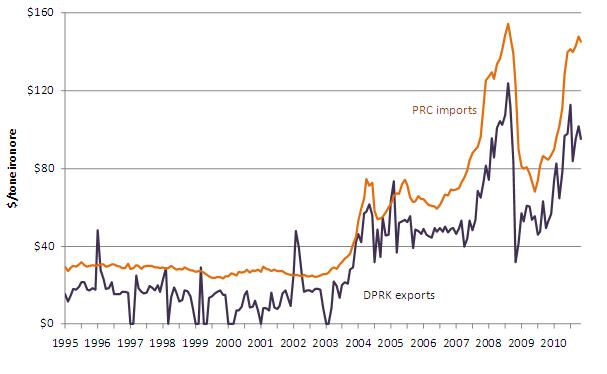
China imports large quantities of iron ore to support its massive steel industry. In the first eleven months of 2010, China imported 465 million tonnes of iron ore, of which 2 million tonnes were from North Korea. Between 1995 and 2010, North Korea’s iron ore exports to China have been consistently discounted when compared with China’s total global iron ore imports. Figure 19 illustrates the consistent disparity between prices reportedly paid for North Korean iron ore versus average prices paid by China for iron ore imports from all countries.
Figure 19: Average Monthly DPRK Iron Ore Prices Compared to Overall PRC Import Prices (January 1995- November 2010)
International iron ore prices rose and became more volatile after 2007. The average price of Chinese iron ore imports rose from $80 to $127 per tonne between 2009 and 2010, while the average price for North Korean iron ore rose from $55 to $93 over the same period. Four possible explanations for the persistent discount include: limited North Korean ability to access export markets, lower transport distances than other iron ore sources such as Brazil, lower iron content per tonne of ore, and/or intentionally agreed-upon discount pricing arranged between Beijing and Pyongyang. The price differential shown in Figure 19 does not appear to be rooted in lower-quality North Korean iron ore. Whereas 65% of DPRK iron ore exports to China in 2010 had at least 60% iron content by mass (HS category 26011110), only 9% of gross Chinese iron ore imports had such high iron content over the same period. The 2010 price differential is also manifested in the high-iron-content ore (HS category 26011110) trade data: North Korea was paid an average $111 per tonne while the average Chinese import price for all countries including the DPRK was $130 per tonne.
5.Infrastructure and other commodities trade
North Korea is a net importer of food, energy-intensive and related goods from China (Figure 2). Although the DPRK recorded a brief $50 million food export surplus in 2004, Nicholas Eberstadt argues that DPRK food exports have more to do with “caloric arbitrage” than agricultural surplus, per se. [16] Eberstadt’s argument is supported by the dominance of cereals in DPRK imports and fish and seafood in North Korean exports to China. The overall trend has been one of increased dependence on China for food–the value of food imports to the DPRK from China grew at an average annual growth rate of 16% between 2000 and 2009. North Korea’s food trade deficit with China expanded from $65 million in 2000 to $150 million in 2009.
Beyond food, trade data indicate that North Korea is investing in its information and communication infrastructure. The value of North Korea’s computer and component imports grew by an average 61% per year between 2005 and 2010. In 2010 the DPRK imported more than a million computers and components from China, of which 86% were data storage devices with an average price of $34 per unit. Computer and component imports were supported by investment in communication infrastructure. The largest sub-category of electrical machinery imports in the first eleven months of 2010 was comprised of “electric apparatuses for line telephony or telegraphy, telephone sets, teleprinters, modems, facsimile machines” (HS category 8517). Between 2000 and 2010 the value of North Korean telephone and equipment imports grew by an average annual growth rate of more than 40%.
5.1Transportation equipment
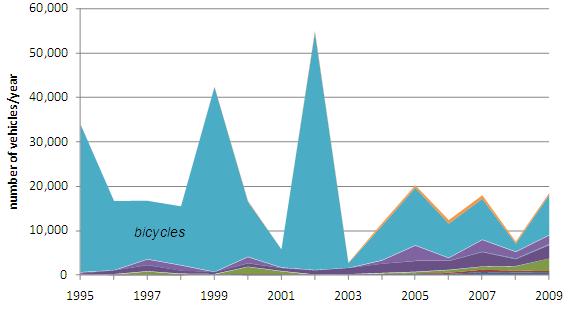
Transportation infrastructure is closely related to the energy and fuels trade, both in terms of providing manufacturing and fuel transport inputs for energy commodities, and in terms of demand for liquid transport fuels. Because DPRK transport exports to China are negligible, this analysis focuses on imports. Transportation equipment and infrastructure imports provide a window to the DPRK’s domestic economic development and to the degree of North Korea’s dependence on China. Figure 16 illustrates the diminishing importance, in recent years, of bicycles in North Korean imports of Chinese transport equipment by quantity.
Figure 20: Annual Volume of DPRK Transport Vehicle and Equipment Imports from the PRC (1995-2009)
The bicycle portion of North Korean transport imports diminished from 74% in 2000 to 49% in 2009. In 2009 the DPRK spent $410,000 on 9,000 bicycles for an average price of $45 per bicycle. Annual trade data indicate that demand for motorized vehicles is rising in North Korea. The car and truck portion of transport imports (the dark blue and green portions of Figure 16, respectively) grew from 14% by volume in 2000 to 32% in 2009.
In value terms, truck and car imports have come to dominate DPRK-PRC transport trade. The car and truck portion of imports by value almost doubled from 46% in 2000 to 83% in 2009. While the average price per car grew at an average annual growth rate of 9% between 2000 and 2009, it appears that North Korea did not start importing new luxury vehicles (or at least, a significantly higher proportion of such vehicles) insofar as the average price of imported Chinese cars was $10,000 in 2009, up from $4,700 per vehicle in 2000. In 2009 86% of imported cars were mid-sized spark-ignition vehicles with engine capacity of 1.5 to 3 liters. [17] Three quarters of North Korean 2010 truck imports were large cargo trucks over 20 metric tonnes of gross vehicle weight (HS category 870423). The increase of truck imports by 28% per year between 2000 and 2009 combines with expanding oil product imports to suggest growth of North Korea’s road transport sector, although a decline in the DPRK’s domestic road vehicles industry may also be a factor in this pattern.
5.2Energy-intensive commodities
Growth of North Korean mineral exports and mining and transport equipment imports is consistent with the larger shift in the bilateral trade relationship toward more resource exports from the DPRK to China, and more energy-intensive manufactured imports to the DPRK from China. Figure 22 illustrates the annual value of energy-intensive bilateral trade between 1995 and 2009. [18]
Figure 22: Annual Value of Energy-Intensive DPRK Trade with China (1995-2009)
The value of energy-intensive imports grew by an average annual rate of 19% between 2000 and 2009, when it reached $590 million. The 2009 value of North Korean energy-intensive exports was $98 million, most of which was comprised of iron and steel. An interesting question for future research is the extent to which the energy embodied in North Korea’s increasing manufactured imports counter-balances net exports of energy embodied in energy and fuels exports.
6.Major trends and implications
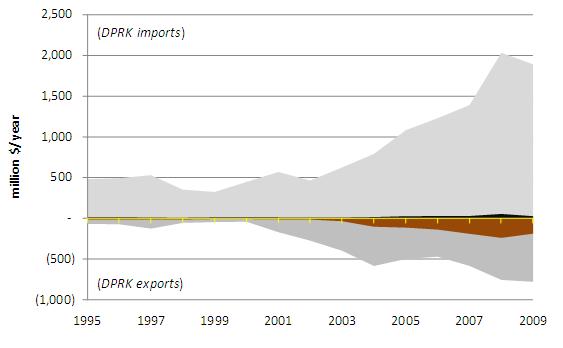
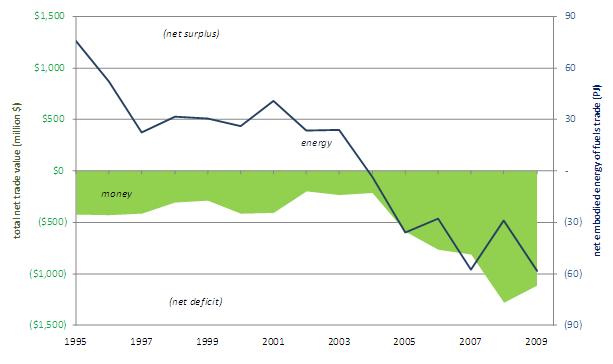
The most concise, and perhaps most salient, metric of Sino-DPRK trade is the scale of North Korea’s annual trade deficit. The DPRK has run a financial deficit in its bilateral trade with China since 1995. After 1995 the energy content of North Korea’s net fuel imports dropped steadily until it became a net energy exporter in 2004. Figure 23 shows the growth of North Korea’s monetary deficit to a fourteen-year high of $1.3 billion in 2008, as well as the transition from energy surplus to energy deficit in 2004. Given that North Korea’s total primary energy supply was estimated at 18 Mtoe in 2007 (IEA, 2009), the country exported about 7% of its TPES to China in 2007 in the form of net energy and fuel exports, mostly as coal. It should be noted that the embodied energy deficit in Figure 23 is limited to energy and fuels trade and would be diminished if this embodied energy analysis also included manufactured goods such as those described in Figure 22. Insofar as North Korean monetary trade deficits are a “proxy for political strength,” Pyongyang may be thriving on the expanding bilateral trade relationship (Eberstadt, 2006). The juxtaposition of expanding monetary deficits with growing net transfers of energy and minerals from North Korea to China suggest that a de facto barter arrangement has emerged whereby Chinese oil, machinery, manufactured goods, and food are exchanged for North Korean coal, minerals, and other natural resources.
Figure 23: Financial and Energy Balance of Bilateral China-North Korea Annual Trade (1995-2009)
The data caveats listed in Section 2 notwithstanding, Chinese customs data tell a coherent story about bilateral trade and the changing characteristics of North Korea’s economy and energy system. There are four basic points in this story: net energy and fuels flows have reversed with the DPRK’s emergence as a coal and electricity exporter; in terms of unit prices, the DPRK is “selling low and buying high” in energy trade with China, though the margins are shrinking; imports are becoming more industry-intensive and exports more mineral- and resource-intensive; and aggregate bilateral trade deficits are large and growing. Overall, Chinese customs data suggest that North Korea is trading the regime’s political present for the country’s energy and economic future.
III. Acknowledgements
The research described in this paper was supported in part by the Nautilus Institute for Security and Sustainability, and is based on research carried out by the author for the DPRK Regional Energy Security Project. The author gratefully acknowledges David Von Hippel for his suggestions and editorial assistance.
N. Eberstadt, “North Korea’s Interlocked Economic Crises,” Asian Survey 38, no.3 (1998): 203-230.
N. Eberstadt, “Nuclear Shakedown,” Wall Street Journal (July 6, 2006): A14.
International Energy Agency (IEA), Energy Balances of Non-OECD Countries (Paris: IEA, 2009)
Lucy Hornby and Jack Kim, “North Korean coal exports to China hint at barter,” Reuters, August 4, 2009.
M.E. Manyin and M.B. Nikitin, Foreign Assistance to North Korea (Washington, DC: Congressional Research Service, 2010).
D.K. Nanto and E. Chanlett-Avery, The North Korean Economy: Background and Policy Analysis (Washington, DC: Congressional Research Service, 2005).
David von Hippel, et al., “International energy assistance needs and options for the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (DPRK)”, Energy Policy 36 (2008): 541-552.
[1] The value of inter-Korean trade reached $1.7 billion in 2009, compared to $2.7 billion for DPRK-PRC trade; http://english.yonhapnews.co.kr/business/2010/04/28/99/0503000000AEN20100428002300315F.HTML. (accessed March 9, 2011)
[2] Data on aggregate U.S. assistance to North Korea are published in Manyin and Nikitin (2010).
[3] Monthly exchange rates of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York are available at http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/g5/current/.
[4] Chris Buckley, “China hides North Korea trade in statistics,” Reuters, October 26, 2009. http://in.reuters.com/article/worldNews/idINIndia-43430320091026 (accessed March 9, 2011)
[5] In Figure 2 “energy and fuels” is comprised of mineral fuels, oils, waxes, and bituminous substances (HS category 27).
[6] The four categories in Figure 2 encompass all reported DPRK-PRC trade. Energy intensive and related goods is comprised of iron & steel products, railway materials, and ships & boats, machinery, electrical machinery, unfinished iron & steel, vehicles (not railway), fertilizers, paper & paper products, aluminum, glass, stone products & cement, and aircrafts & spacecrafts; food includes meat, cereals, milling, malt, and starch products, fats & oils, grains, beverages, vegetables, salt, prepared meats & fish, fish and seafood, food waste & animal feed, edible fruit & nuts, sugar, miscellaneous foods, preserved food, spices, coffee, tea, cocoa, dairy, eggs, honey, live animals, and other vegetables; and other is a residual aggregation of the remaining 62 HS 2-digit level categories, largely composed woven apparel, manufactured goods, and minerals.
[7] The categories in Table 1 correspond to two-digit HS commodity classifications.
[8] Figure 3 through 5 cover trade in coal, coke, crude oil, and oil products. Minor energy and fuels categories are not included, namely: mineral tars, petroleum jellies, petroleum coke, pitch, and bitumen products.
[9] This analysis assumes the following energy densities: 25 gigajoules/tonne coal; 17 GJ/tonne lignite; 28 GJ/tonne coke; 42 GJ/tonne crude oil; and 45 GJ/tonne oil products as per DPRK values from International Energy Agency, Energy Balances of Non-OECD Countries, (2009): available at: http://bioenergy.ornl.gov/papers/misc/energy_conv.html and http://energy.usgs.gov/glossary.html. (accessed March 9, 2011)
[10] Lucy Hornby and Jack Kim. “North Korean coal exports to China hint at barter,” Reuters, August 4, 2009.
[11] The largest growth of generator set imports over this period was in category HS 850212, which includes agricultural generator sets, air conditioner passenger car diesel generating sets, coal-fired generator sets, diesel generating sets, and engineering machinery generator sets from 75 to 375 kVA.
[12] David von Hippel, et al., “International energy assistance needs and options for the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (DPRK)”, Energy Policy 36 (2008):541-552.
[13] In 2009 anthracite coal from North Korea comprised 10% of China’s total global anthracite coal imports.
[14] A Mill is equal to one tenth of a U.S. cent, or $0.001.
[15] Within this analysis minerals are comprised of stone, plaster, and cement (HS 68), ores, slag, and ash (HS 26), inorganic chemicals and rare earth metals (HS 28), precious stones and metals (HS 71), copper (HS 74), nickel (HS 75), lead (HS 78), zinc (HS 79), tin (HS 80), and other base metals (HS 81).
[16] N Eberstadt, “North Korea’s Interlocked Economic Crises”, Asian Survey 38, no.3 (1998): 203-230.
[17] HS trade categories do not differentiate between new and used vehicles.
[18] Energy intensive and related goods is comprised of iron & steel products, railway materials, and ships & boats, machinery, electrical machinery, unfinished iron & steel, vehicles (not railway), fertilizers, paper & paper products, aluminum, glass, stone products & cement, and aircrafts & spacecrafts. This category is not all-inclusive.
VI. Nautilus invites your responses
The Northeast Asia Peace and Security Network invites your responses to this essay. Please send responses to: bscott@nautilus.org. Responses will be considered for redistribution to the network only if they include the author’s name, affiliation, and explicit consent.


One thought on “North Korean Trade with China as Reported in Chinese Customs Statistics: 1995-2009 Energy and Minerals Trends and Implications”